Self-Host
Upgrade
BEFORE YOU UPGRADE
- Never run multiple containers on the same data directory. Stop and remove the old one first to avoid corruption.
- Back up your metadata before upgrading. You’ll need it if you ever downgrade.
- Verify the upgrade in a test environment first.
Back up Data
External PostgreSQL Metadata (Recommended)
If--pg is specified, the metadata will be stored in the specified external PostgreSQL database. Below shows how to back up and restore the Bytebase metadata, let’s assume the metadata is stored in metadb.
Back up the metadata
Restore Option 1 - Restore to the same metadb
Step 1 - Restore metadata to a temporary db
Create a new dbmetadb_new:
Step 2 - Swap the existing metadata db with the temporary db
You need to first stop Bytebase otherwise its connection to the metadata db will prevent renaming the database.Also, you can not rename the connecting database so you need to connect to the PostgreSQL instance using a different database like
postgres.metadb to metadb_old:
metadb_new to the metadb, which will serve as the new metadata db:
Step 3 - Drop the old metadata db
Restart Bytebase and verify the metadata is restored properly. Afterwards, you can drop the old database:Restore Option 2 - Restore to a different database metadb2
Step 1 - Modify the dump file
The dump file records the Bytebase metadata schema change history, and it’s database specific. So we need to change the existing record value frommetadb to metadb2 first, which means to transfer
the change history to metadb2.
Locate the migration_history table in the dump file, and for each record, find the value metadb
which corresponds to the namespace column, change each occurrence from metadb to metadb2.
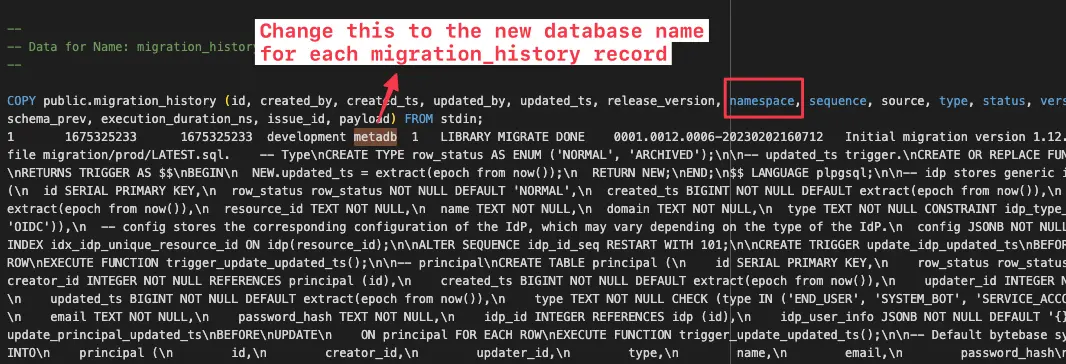
Step 2 - Restore metadata to metadb2
Create a new db metadb2:
Step 3 - Drop the old metadata db
Restart Bytebase and verify the metadata is restored properly. Afterwards, you can drop the old database:Embedded PostgreSQL Metadata
If External PostgreSQL is not configured, then Bytebase will store the metadata under the--data directory.
You can back up the --data directory or the pgdata subfolder.
You should periodically back up the entire
--data directory if any data is stored there.If Bytebase is running and not in the --readonly mode, and you want to take the backup, then the underlying data volume must support snapshot feature where the entire directory can take a snapshot at the same time, otherwise it may produce a corrupted backup bundle.Upgrade Process
Take Docker as an example (follow the below steps exactly):-
Stop Bytebase
-
🚨 Back up the Bytebase metadata
Above example backs up the metadata stored in the embedded database. If you store metadata in the external PostgreSQL, you should back up that database using the instructions in the “Back up Data” section above.
- Change version string to 3.9.0
-
Start Bytebase
Version Management
Bytebase adopts Semantic Versioning using the MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH format. Bytebase ties the version number with the underlying database schema progression, because:- Schema change is a good approximate to the functional change. Large schema changes often indicate large functional changes.
-
Schema change determines the customer involvement when upgrading to the new version.
MAJORversion change usually happens once a year. It might require manual effort from the customer. Bytebase will try to avoid that if possible.MINORversion is changed when the underlying database schema changes. While the upgrade does not require customer involvement.MINORversion change usually happens about once every month.PATCHversion is changed when the new version does not include underlying database schema changes.PATCHversion change usually happens bi-weekly following our release schedule.
Docker Image Version
Certain changes maybe cherry-picked into the existing version. So when Bytebase starts next time, it will self-upgrade. If you don’t want this behavior, you could use the image digest to pin the exact commit. For example,org.opencontainers.image.revisionis the git commit hash, in the example, it corresponds to the particular git commitorg.opencontainers.image.versionis the release version, in the example, it corresponds to the 3.7.0 release branch.
Upgrade from Old Version
To upgrade, replace the version string with the target version and restart. Bytebase will self-upgrade automatically.Upgrade from 1.x or 2.x
First upgrade to 2.1.0 and then follow the next section.Upgrade from 3.0.0 ~ 3.3.0
First upgrade to 3.3.1 and then follow the next section.Upgrade from 3.3.1
Replace the version string with the latest version and restart.Downgrade
Downgrade is as dangerous as upgrade, we highly recommend you verify the downgrade in a test
environment first.
Downgrade PATCH Version
Downgrades carry the same risks as upgrades, so validate any downgrade in a test environment before proceeding.Downgrade MINOR Version
Minor version upgrade/downgrade involves metadata schema change, so we must restore the metadata database to the old version first. Thus the metadata backup for the old version must be available.- Stop Bytebase
- Restore the metadata database with the metadata backup
- Replace the version with the old version.
- Start Bytebase

